- Zola vs MyRegistry: Which is the Best Registry for 2024? - November 30, 2023
- Best Art Deco Wedding Band Ideas - April 23, 2023
- Jade vs Emerald: Which Green Gemstone Is the One for You? - April 23, 2023
It’s time to choose that ring you’ve always dreamt about, whether it’s an engagement ring, an eternity ring, or you’re merely shopping for something to commemorate another special occasion. Either way, you’re going to want to research stones, their meaning, their cost, and origin before committing to spending.
Irrespective of how big or modest your budget is, it’s wise to have all the information you need before going ahead. Traditionally, we all know that diamonds are the go-to for big occasions. Many of us dream of having a big rock on our finger that we wear for the rest of our lives.
However, rather than going straight down the traditional route, why not explore some other options, especially if your budget is more modest. Two possibilities you could consider are white sapphire and cubic zirconia. Both are often touted as cheaper alternatives to diamonds, and both are widely available. However, there are things you need to look out for before buying, and we’re going to take a good look at each right here and give you the low-down.
After all, whatever price you want to pay, you’re still going to want to see that you’ve bought a quality product, right? So let’s get going and delve into these stones and what they’re all about…
Main Differences Between White Sapphire vs Cubic Zirconia
The main differences between white sapphire vs cubic zirconia are:
- White sapphire is found naturally using mining techniques, whereas cubic zirconia is artificially created.
- White sapphire has the highest refractive index out of all-natural gemstones, whereas Cubic zirconia has an even higher refractive index, which makes it look more like a diamond.
- White sapphire is a hard stone similar to a diamond, whereas Cubic zirconia is softer and is, therefore, more likely to suffer from scratches.
- White sapphire is usually a pricier option, whereas cubic zirconia tends to be the cheaper of the two.
Now we’ve covered the critical differences between these two stones, let’s look at each in more detail.
What’s White Sapphire?

White sapphires have no color. When we think of sapphires, it’s usually of the bluestones, for example, the one Kate Middleton wears as her engagement ring that belonged to Princess Diana. Still, the reality is that they come in a range of colors, including pink, green, yellow, and, of course, white.
The stone is part of a family of natural minerals called the corundum family. This is the family to which rubies and blue sapphires also belong. The stone is a kind of aluminum oxide that has traces of copper, chromium, iron, magnesium, and titanium in it. If you imagine the colors of each of those, it all depends on how much trace sapphire it contains. This is the color it will be. So, a yellow stone will naturally have more copper in it.
White sapphires don’t cost as much as diamonds, so they are often seen as a natural but more affordable alternative to diamonds. So, if you’re someone who absolutely doesn’t want a human-made ring on their finger, then it’s worth looking at natural white Sapphires as an option for that unique ring. That said, there are some things you need to consider before investing.
It’s worth knowing when you get a white sapphire; it’s actually a colored stone that has been chemically or heats treated to get it to its clear state. So although it starts out life as natural stone, it’s adjusted by a chemical process to achieve its bright look to mimic its diamond competitors.
However, don’t be fooled into thinking all sapphires are real. There are two kinds of white sapphire: real (or natural) ones, or the ones created in a laboratory (lab created diamond).
Both types of stone are made from corundum. They’re indistinguishable from each other in terms of what they look like and their hardness. We cover how the synthetic versions are made a bit further down.
Check out Blue Nile's selection of White Sapphire jewelry and find the accessories that match your style!
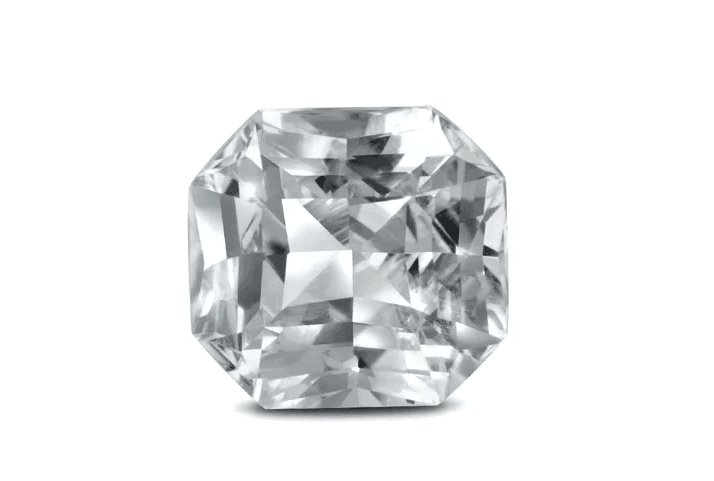
What Does a White Sapphire Look Like?

If you compared it to a diamond or a CZ stone, you’d see that it looks less bright. It can often have a milky hue or look a bit cloudy. A CZ stone will appear more sparkly and light reflective.
What’s Cubic Zirconia?
Here we have a synthetic stone that is often marketed as an affordable alternative to diamonds and frequently compared to diamonds. Cubic zirconia is also known as CZ. If you see pictures of it, you’ll notice how sparkly and reflective it is. It’s not a natural stone. However, it’s entirely and totally human-made crystalline material. It’s a hard stone and without color. However, it is now made in different colors as well using oxides throughout the production process.
A cubic zirconia stone is flawless. Its perception over time has changed. For some people, it’s the real-deal diamond or sapphire and nothing else. However, a CZ stone is less expensive and can look just as amazing.
So, where does CZ come from? It was discovered in the 1800s, but it wasn’t until much later in 1976 that it hit the mass-production market. The reason it finally surfaced as a viable alternative to the more expensive options is that its hard-wearing, hard, cheap, and long-lasting. And, of course, it’s hard to discern a difference between it and it’s more expensive counterparts. A layperson will struggle to tell the difference; it’s really only jewelers and experts who have the right tools to hand to tell the difference.
One thing worth noting is that you shouldn’t confuse Cubic Zirconia with Cubic Zirconium. They are quite different from each other. Cubic Zirconium does play an essential part in the creation of CZ stones, however. It’s a metal, and when it’s in a powder, it’s mixed and heated at 4982F with Zirconium Dioxide to make Cubic Zirconia.
If you’re after a colored CZ stone, then that’s also possible, as we already mentioned. Basically, a colored version is made by adding different elements to the production process to create a colored stone. For example, you can add chromium to make the stone green.
Put simply; a Cubic Zirconia is a lovely, affordable, and ethical alternative to mined stones. It’s flawless; it’s ethical, it’s kind on the wallet, what’s not to like? Yes, people are less sentimental about it, and it doesn’t have the same romantic connotations as sapphires and diamonds, but it still looks great!
What Does a Cubic Zirconia Look Like?

It’s very sparkly! If you imagine a real diamond, that has a refractive index of 2.42, and Cubic Zirconia comes in close with a 2.15-2.18 score. Now look at white sapphires, and they sit at only 1.76 on the index.
Where Does White Sapphire Come From?
Traditionally the white sapphire is associated with wisdom, intuition, and clarity. It is often associated with being a symbol of power, strength, wise judgment, and kindness. Legend has it that the Ancient Greeks discovered the stone on the Cycladic island of Naxos.
It was associated with the Greek god Apollo, who was the god of the Sun and light, prophecies, healing and diseases, truth, music, and dance. In mythology, white sapphires were offered up to the Delphi Oracle as a way of hoping that Greek warriors would be kept safe from harm. It’s also thought that Greek warriors would give their wives a sapphire necklace to ensure their fidelity.
White sapphires are often associated as the natural gemstone for people born under astrology signs of Taurus and Libra, so if you’re into your star signs, now you know! Today, most natural sapphires are mined in Africa, the Middle East, South East Asia, and parts of Western USA.
As far as synthetic or lab-grown sapphires are concerned, their production began when synthetic forms of corundum were discovered in the late 1800s. They are generally seen as a cheaper alternative to natural sapphires.
The lab-created sapphires are produced to look just like the real thing (diamond simulant vs mined diamond). They are relatively flawless, meaning it would be hard for an untrained eye to tell the difference between a natural and a lab-created sapphire. Lab-created sapphires are created in two different ways; these are called melt processes and solution processes.
The melting process is where aluminum oxide is melted onto a sapphire droplet. This is also called Flame Fusion and is the cheaper way of making sapphires. A flame melts aluminum oxide powder, which creates a sizeable tear-shaped droplet. Another melt process uses radio waves rather than fire to melt the aluminum oxide.
The solution process is where sapphire crystals are grown in a solution. This process is one that tries to mimic what happens when crystals are formed naturally. Aluminum oxide is subjected to intense heat and pressure in a kind of “pressure cooker.”
Brilliant Earth's jewelry is not only conflict-free, but it also allows you to create your own pieces. Simply select your gemstone, setting and complete your ring!
Where Does Cubic Zirconia Come From?

Cubic Zirconia is made or grown in a lab. It’s made by combining zirconium oxide powder with magnesium and calcium, which are then heated at a temperature of 4982F. The process varies from lab to lab. It was first made in 1976 and had a hardness rating of 8.5-9, whereas diamonds hit a 10.
However, Cubic Zirconia’s history dates back to 1976. In 1937 two German gemologists found that when zirconium oxide was melted, it had cube-shaped crystals. However, nothing happened following this discovery until the 1960s when the same discovery was made by scientists who were looking for cheaper materials to produce lasers.
Fast forward to Russia and 1977, when Russian scientists found a way of growing these crystals using a synthetic process. They called the diamonds Djevalite. However, it wasn’t until the 1980s when these stones became fashionable (thanks to Swarowski). This household brand created its own version of cubic zirconia, and it was during this time that the crystal became a popular and cheaper diamond substitute.
So how’s it made? Again, it’s pure science! Cubic Zirconia is formed in a machine called a skull crucible. Zirconium oxide powder is put inside the crucible, and then a tiny amount of calcium is added. This acts as a stabilizer, and as a result, the zirconium oxide takes on the molecular structure needed for scientists to create the CZ stone.
Read More: Moissanite vs Cubic Zirconia: Which is Best for You?
How Are Sapphires and Cubic Zirconia Stones Graded?

All stones, be they natural or synthetic are graded according to their:
- Clarity
- Color
- Cut
- Carat
It’s worth bearing in mind, the weight of synthetic gems is higher than natural stones because the materials they’re made from are denser. When we talk about clarity, we mean how transparent the stone is. If the stone is mined naturally rather than lab-created, then its clarity is determined by nature. Basically, the clearer a stone is, the more it’s worth.
When we talk about color, in the case of white sapphires and CZ stones, they are clear. Generally speaking, white or clear stones represent higher value. The cut of the stone will determine how brilliant it is.
Both sapphires and cubic zirconia are measured in carats. The higher the carat, the higher the value and cost. However, gems vary in density. So, for example, if you were to compare a sapphire to a diamond, then a sapphire is usually smaller because sapphires tend to be heavier and so they are smaller than diamonds. So a diamond and a sapphire of the same carat will be different sizes. A sapphire’s density is 3.98 g/cm3.
As for cubic zirconia, the higher the carat, the less it starts to resemble a natural stone such as a sapphire or, more commonly, a diamond. Just like our comparison above, a CZ stone is denser than a diamond and, therefore, more substantial. A cubic zirconia stone’s density is 5.5-5.9, making it more substantial than a sapphire.
The Pros And Cons of Each
Before investing in either a natural or synthetic stone, it’s worth having a real look at the pros and cons of each, so we’ve listed what we think these are below as bullet points:
White Sapphire: Pros
- The synthetic version is easier on the wallet
- Real version won’t lose its brilliance or shine
- Synthetic sapphires are less likely to get scratched or chip
- It’s more durable
- Genuine sapphires are a good diamond alternative
White Sapphire: Cons
- Synthetic sapphire doesn’t retain its brilliance or hue
- Needs frequent gently cleaning
- Can appear frosted because of wear and tear
- Natural sapphires are rare and therefore expensive
- Not as hard as diamonds
- The synthetic version has less sentimental value than the real thing
Cubic Zirconia: Pros
- Hardness is close to that of diamonds
- Brilliance /refractive index is high
- Flawless
- Cheaper than diamonds
- Strongly resembles diamonds
Cubic Zirconia: Cons
- For purists, there’s nothing like a real diamond or sapphire
- It’s not as hard as a diamond
- Will become cloudy over time
- Costs less but it’s also less valuable
- Wears down quicker than sapphires
- It’s more porous and therefore eventually need to be replaced
- Less sentimental value than a natural stone
White Sapphire Hardness, Refraction and Value
On the MOHS scale, it measures as a nine. Its value increases the more carats it has. The stone has a refractive index of 1.76-1.77. Natural sapphires come cheaper than natural diamonds, and typically we’re talking around $500-$1500 per carat. White sapphires come less expensive than blue sapphires, which cost more than twice the price.
One important thing to note is, the GIA (Gemological Institute of America) does not grade sapphires. It does offer reports on the stone that relate to its carat, color, shape, and if it’s been heat-treated or not.
Like diamonds, white sapphires are graded based on their appearance. So, the highest rating a sapphire can get is an AAA; the lowest is A. The whiter and brighter the sapphire, the higher the grade.
Cubic Zirconia Hardness, Refraction and Value
Cubic Zirconia measures 8.5-9 in terms of hardness and has a refractive index of 2.15-2.18. In terms of its value, like natural stones, the prices vary, and the grade of the stone varies. It’s possible to buy a CZ stone for tens of dollars per carat to much more depending on the grade of the stone.
Cubic Zirconia stones are also graded. Typically, they come in A, AAA, and AAAAA grades, and again, the better the quality, the more As a CZ stone will have! The lower the A grade, the more likely the stone will chip and change color. It’ll also be the cheapest kind you get. The higher-grade CZ stones usually hand polished and hand-cut.
Comparing The Two

Next to diamonds, sapphires are the second hardest stones in the world. If a rock is soft, it’s more likely to be damaged. It’s that simple. Diamonds are ten on the Mohs scale, and sapphires are around 9. Cubic Zirconia is softer than white sapphire and is approximately 8 and 8.5. Cubic Zirconia is still thought of as a hard stone, however. It’s just a bit more susceptible to being scratched than a sapphire.
As for brilliance, cubic zirconia is sparklier than a sapphire, but if a sapphire is cut into a round shape, it can appear quite sparkly. Neither stone is as sparkly as a diamond, although cubic zirconia comes close.
Cubic zirconia will sparkle as long as it’s kept clean and you look after it well. It has more light dispersion than white sapphire, and the same applies to it when compared with diamonds. Basically, dispersion is the prism effect you get when white light enters the stone; the light breaks into a full range of colors that are reflected your eye. It’s this sparkle that people talk about when referring to a stone’s “fire.”
Caring for White Sapphires and Cubic Zirconia Stones
The one word we’d use here when talking about looking after your gems is “carefully.”
When cleaning your cubic zirconia, the best way is to use a conventional jewelry cleaner or gentle soap and soft cloth and/or toothbrush. If you get dirt on the stone, you can always just brush it off because the rock is so hard. It’s also essential to make sure that you get rid of all the soap or detergent during the cleaning process and then wipe the stone dry so that it keeps its brilliance. It’s worth cleaning cubic zirconia regularly even to remove natural oils from your skin, which may dull the appearance of the stone.
If we’re talking about sapphires, well, because they are made from corundum, which next to diamonds is the second hardest gem in the world, then that makes it pretty tough, right? It means it’s harder to scratch and break. The simplest way to clean a sapphire is with warm soapy water and then wipe and dry it with a gem cleaning cloth.
You can also use a soft brush to clean the setting and get rid of any dust or dirt. You don’t need any chemicals like bleach or abrasive cleaners when cleaning this stone. If you’re storing your sapphire jewelry with other pieces, remember that it’s a hard stone. Keep it separate, so it doesn’t scratch any other parts. You can also soak your sapphires in warm soapy water too for up to 15 minutes.
In the case of both stones, it’s always a good idea to take them off when you’re showering, playing sports, or doing things like gardening. Pretty much anything where sweat and dirt may invade the setting and damage the stone.
FAQ’s: White Sapphires and Cubic Zirconia’s
Here are a few of the most frequently asked questions about these two types of rocks:
Why does cubic zirconia look more like a diamond than white sapphire?
It comes down to the refractive index. The index of a traditional diamond is 2.42, and cubic zirconia usually ranges from 2.15 to 2.18, whereas a white sapphire is only 1.76. Consequently, cubic zirconia shines more, which gives it a more diamond-like appearance.
What about longevity?
No matter how well you take care of it, cubic zirconia loses its shine over time. It can become clouded and lose its color. Alternatively, a white sapphire will look as good as new for years to come.
Is white sapphire a good option for an engagement ring?
It comes down to preference. However, it’s not a popular choice because the stone lacks brilliance – especially when compared to zirconia with its gorgeous shine, the white sapphire looks lackluster.
Why’s cubic zirconia cheaper?
While it looks like a diamond at first, it’s easy to ruin a zirconia stone. It doesn’t have the same longevity natural stones boast. Not to mention, it’s made in a lab, so none of the mining work is required, which again makes it a more affordable option.
Which is a better diamond alternative?
It’s entirely up to the buyer. Zirconia is cheaper, while white sapphires are cloudier. One has a look of a diamond; the other has the durability. Only the buyer can decide which is worth more to them.
Which to Choose?
We’re talking here about choosing between three different stones, two of which are lab-created. Our advice is that they all look great, but it’s important to know what you are paying for. If you’re being told you’re buying a natural sapphire, then be sure that that’s the case, as they are extremely rare, and you want to avoid being duped.
If you simply love sapphires and want to wear that stone because it has meaning to you or you want an affordable natural stone, they go for that. If, however, you want something that looks more like a diamond, but you can’t afford a diamond, cubic zirconia should be your go-to-gem. It’s a fabulously affordable diamond alternative.
Whichever stone you go for, do your research, and all the more so when you are buying your gems online. Make sure that whatever you spend your hard-earned dollars on comes with a full guarantee and certificate of authentication.
Check out Blue Nile's selection of White Sapphire jewelry and find the accessories that match your style!
Recommended Reads:
If you love sapphire or cubic zirconia, you would definitely want to check the 5 Unique Blue Sapphire Pendants That Are Way Too Cute and the Best Cubic Zirconia Wedding Rings that go perfectly well together!
Also Read:


